
Whether you call them technician, engineer, analyst, advisor, expert, manager, responsible for …, your organization cannot do without professionals. They are the link between strategic decisions and operations. The value-added of field employees is easy to measure. It is one of the pillars of lean and operational excellence. Similarly, the value of your professionals must also be defined and evaluated. What role do you want them to play, what do you expect from them? What added value do they bring to your organization?
I propose nine roles, classified according to the level of technical competence and the interpersonal skill level. Technical competence is easily defined in relation to your core business. Interpersonal skills are much broader. Two key interpersonal skills of professionals are the ability to:
- understand the needs of their interlocutors, to explain to and support their colleagues (pedagogy)
- rise-up and find new solutions to known problems, in a changing environment (autonomy).
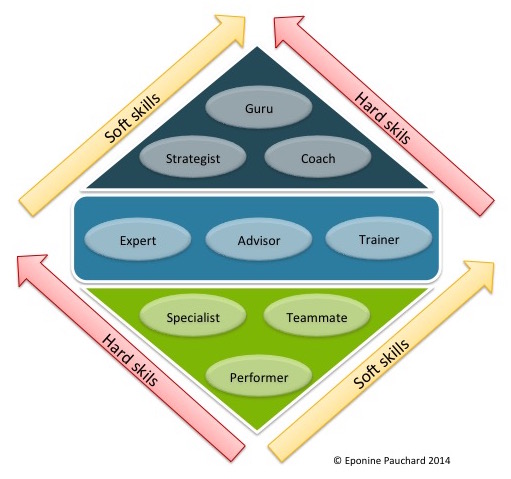
Operational roles
- Executer: it is the beginner, he realizes the requested actions, according to the methods of the organization. He does not bring any judgment. his focus is on delivering on time, at the required level of quality. He does not worry about the links with other colleagues.
- Specialist: he begins to know his subject. He is able to find different solutions in known situations or manage unknown situations from known solutions.
- Teammate: he carries out the required actions and shares the information with his colleagues. He creates links with the rest of the organization, he is able to share information on his subject with others
Tactical roles
- Expert: He knows everything about his subject, he is able to solve any problem in his field.
- Trainer: He is able to transmit knowledge to other people, even without having an extensive knowledge of his subject. Using material developed by content experts, he appropriates the subject. Above all, uses his teaching skills to transmit the elements to his colleagues.
- Referent: at the heart of the diagram, he has a balanced profile between his technical and interpersonal skills. Therefore he is versatile. He is a valued resource because he can solve problems and share with his colleagues. The referent usually has a global vision and knows impacts in the organization.
Strategic roles
- Strategist: he compiles information inside and outside the organization. He knows how to apply his knowledge and has a strategic vision, he is able to influence his colleagues.
- Coach: he accompanies employees and managers in solving their problems. He usually combines pedagogy and strategy to make them think and find the right solutions.
- Guru: ultimate level that an individual can reach. He is the undisputed expert of his field, knows his subject perfectly and is able to popularize it, to make followers. And most of all he can develop other people to reach his level of expertise.

It is important to know what are the skills and strengths of your professionals; as well as define how you want to use them. The same person may have different roles depending on the projects or tasks entrusted to him or her. Always ask yourself about the added value and the good use of your resources!
